Java Programming 2 | Conditionals, Loops, and Debugging
Java Programming 2 | Conditionals, Loops, and Debugging

- Control Flow
(1) The Definition of the Control Flow
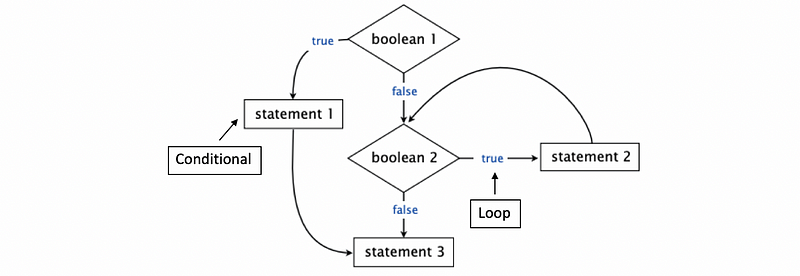
The sequence of statements that are actually executed in a program. Conditionals and loops enable us to choreograph control flow. For example,
2. Conditionals: the if statement
(1) The if Statement
The if statement executes certain statements depending on the values of certain variables. It follows the following steps:
- Evaluate a boolean expression.
- If the boolean is true, execute a statement.
- If the boolean is false, execute the statement behind else.
(2) The if Statement: Example #1 Simulate
The following code simulates a flip coin.
(3) The if Statement: Example #2 Sort
The following code to swap two integers if the first one is greater than the second one.
(4) The if Statement: Example #3 Sort
The following code to sort three integers a, b, and c.
(5) The if Statement: Example #4 Error Checks
Sometimes, we can use the if statement to check the variables.
3. Loops: The while Loop
(1) The Definition of the while Loop
Execute certain statements repeatedly until certain conditions are met.
- Evaluate a boolean expression
- If true, execute a sequence of statements
- Repeat
(2) The while Loop: Example #1 Power
Prints the powers of two from 2⁰ to 2ⁿ.
(3) The while Loop: Example #2 Implement Square Root
The Newton-Raphson method to compute sqrt(c) is:
- Initialize t0 = c
- Set ti+1 to be the average of ti and c / ti
- Repeat until ti = c/ti (up to desired precision)
4. Loops: The for Loop
(1) The Definition of the for Loop
The for loop is an alternative repetition structure.
- Evaluate an initialization statement
- Evaluate a boolean expression
- If true, execute a sequence of statements, then execute an increment statement
- Repeat
(2) The for Loop: Example #1 Ruler
5. Nested Conditionals and Loops
(1) The Definition of Nesting
Any “statement” within a conditional or loop may itself be a conditional or a loop statement.
- Enables complex control flows
- Adds to the challenge of debugging
(2) Nesting: Example #1 Gamber’s Ruin Problem
The following code will show us the result of a type of gambling. Look into the result, you can find out that it will never be a good idea to do gambling.
(3) Nesting: Example #2 Income Tax Calculator
Based on the following code, we can calculate the income tax and our real salary automatically.
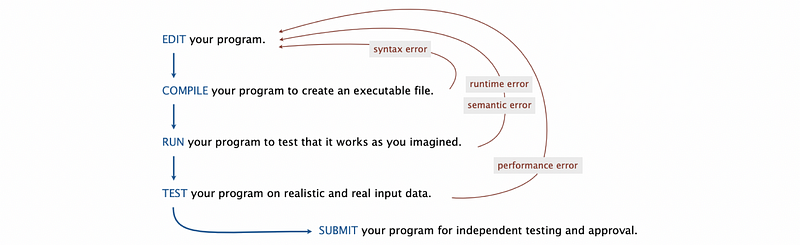
6. Debugging
Is your program a legal Java program? Think about the following sets to debug your program.
- Java compiler can help you find out.
- Find the first compiler error (if any)
- Repeat
- Result: An executable Factors.class file