Linear Algebra 15 | Linear Algebra Cheatsheet
Linear Algebra 15 | Linear Algebra Cheatsheet

- Vector
- Dimension
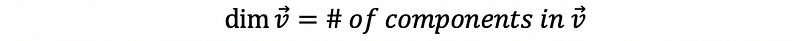
- Linear Combination
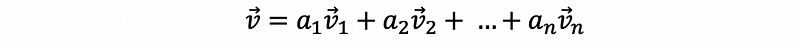
- Dot Product
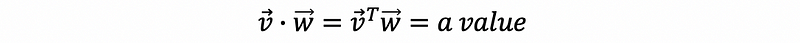
- Outer Product
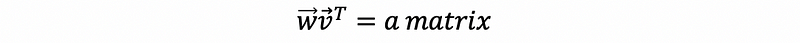
- Norm
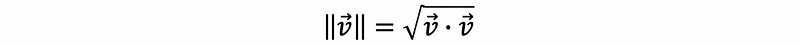
- Scaling
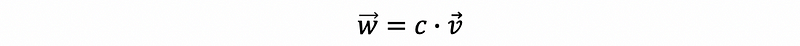
- Rotation
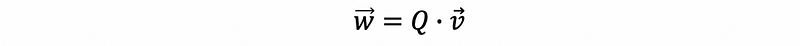
- Projection
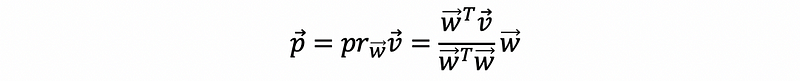
- Normalization (Unity)
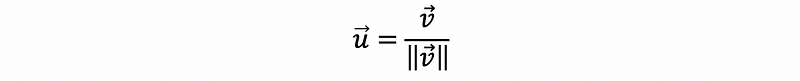
- Perpendicular
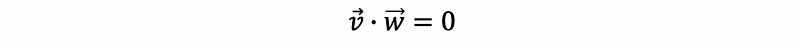
- Schwarz inequality
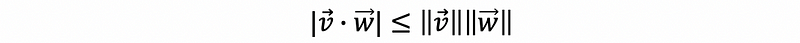
- Triangle inequality
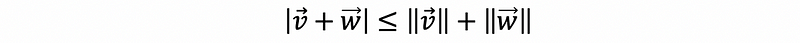
2. Matrix
- Matrix times vector
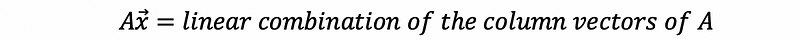
- Associative law
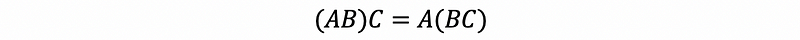
- No commutative law
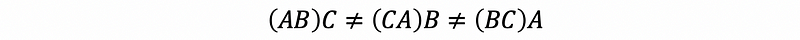
- Pivots
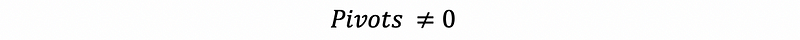
- Identity Matrix
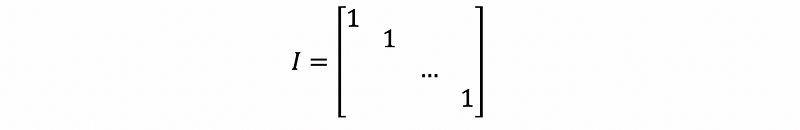
- Elimination Matrix
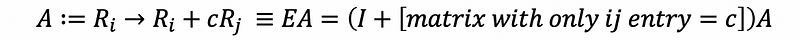
- Inverse Elimination Matrix

- Exchange Matrix
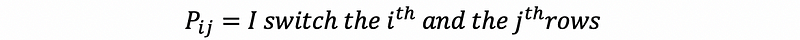
- Augment Matrix

- Transpose Matrix
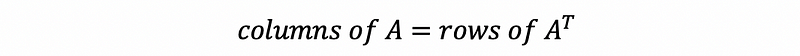
- Inverse Matrix
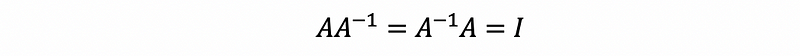
- Transpose Rule
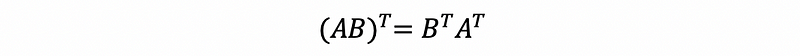
- Inverse Rule
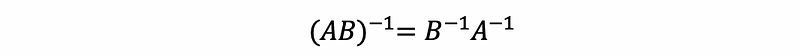
- Invertible Conditions
(1) Pivots: A is invertible if and only if it has n pivots.
(2) Linear Independence: A is invertible if and only if the column vectors of A are all linear independent.
(3) Determinate: A is invertible if and only if det(A) ≠ 0.
(4) Eigenvalues: A is invertible if and only if all the eigenvalues of A ≠ 0.
(5) Definite: If A is a semi-definite symmetric matrix, then A is invertible.
(6) Nullspace: A is invertible if and only if N(A) = ∅.
(7) Diagonally Dominant: If A is a diagonally dominant matrix, then A is invertible.
(8) etc
- LU Factorization
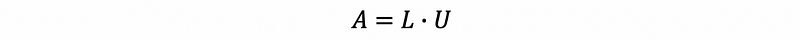
where L is a lower triangular matrix,
and U is an upper triangular matrix.
- Eigendecomposition
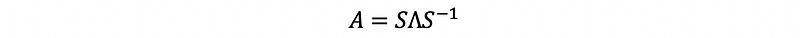
3. Vector Space
- Column space
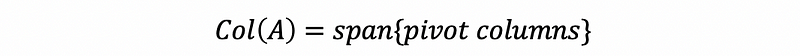
- Nullspace
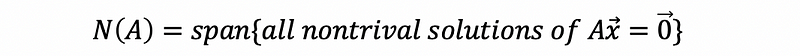
- Row space
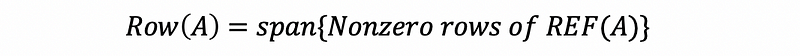
- Left nullspace
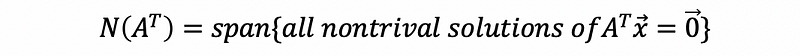
- The dimension of column space
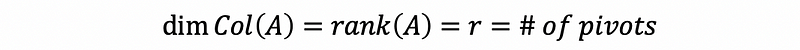
- The dimension of the nullspace
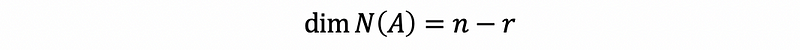
- The dimension of the row space
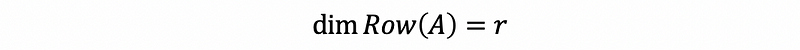
- The dimension of the left nullspace
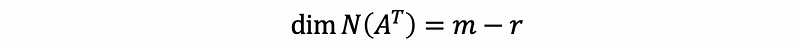
4. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
