Linear Regression 15 | Logistic Regression Inference
Linear Regression 15 | Logistic Regression Inference
- Wald Test of Coefficient
(1) Hypotheses for Wald Test
Similar to SLR and MRL, to tell whether or not a predictor of logistic regression is significant or not, we have to test the parameter of this predictor. The hypotheses of the Wald test is,
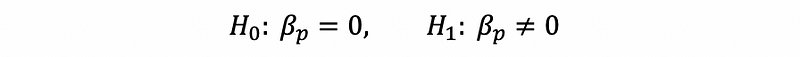
(2) Assumption for Wald Test
The Wald test can only be valid when the sample size is large enough. If we assume that the logistic model is rely on a large sample size, then the MLE is of predicor p follows,
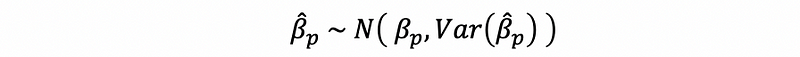
(3) Wald Test
Based on our discussion, we should conduct Z test for the parameter,
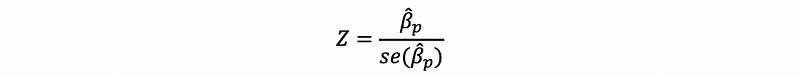
Here, we don’t Then, if
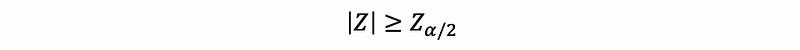
then we can reject H0 and reach the conclusion that the p predictor is significant.
(4) Confidence Interval based on Wald Test
- The confidence level for an estimate
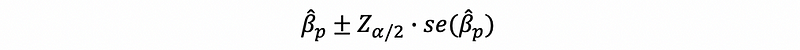
- The confidence level for the odds ratio of an estimate
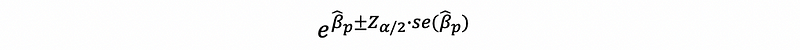
2. Likelihood Ratio Test
(1) Hypotheses for Likelihood Ratio Test
The likelihood ratio test is quite similar to a likelihood version F test with OLSE. Commonly. The null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis are,
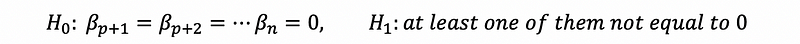
(2) The Definition of Deviance
We don’t have to fully understand this and we only have to know the meaning of this model in a general way. The deviance is defined as the difference of the likelihood value between the fitted model and the saturated model.
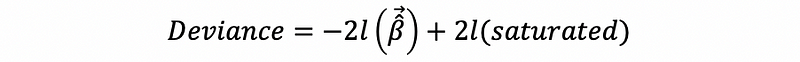
Then, because the second term of this equation is a constant, then the deviance can be simplified as,
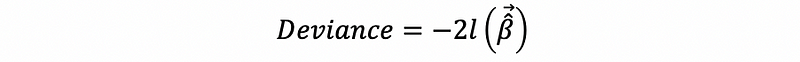
Denote G² as the deviance of the model, then
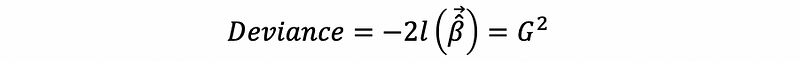
then for the test above, define the test statistics as,
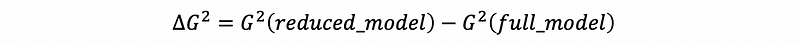
if,
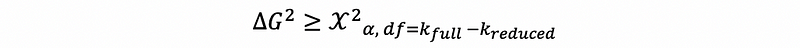
then reject H0, the full model is significantly improved in the likelihood.
3. Deviance Residuals
If we want to evaluate the residuals for the logistic regression model, we have to modify the residuals because they are not the same as the OLS residuals. Basically, there are two commonly used ways for modification,
- Pearson Residuals: this is similar to OLS studentized residuals
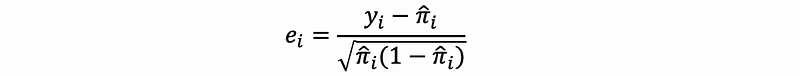
we should observe the person residuals to be distributed horizontally around the ei = 0 line.
- Deviance Residuals
The deviance residuals are defined by,
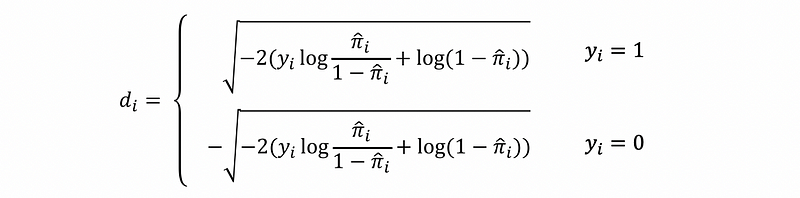
The square of each deviance residual measures the contribution of each response to the deviance of the fitted model.
4. Pseudo R²
Because there’s no OLS principle for the logistic model, then we don’t have the regular R² for us to explain the variance of the model. But there’s actually some pseudo-R²’s that can suggest the goodness of fit for us.
- Efron’s pseudo-R²
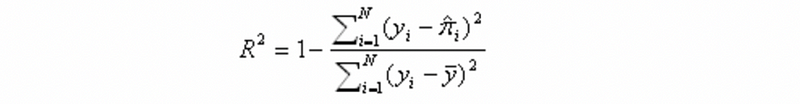
- Mc Fadden’s pseudo-R²
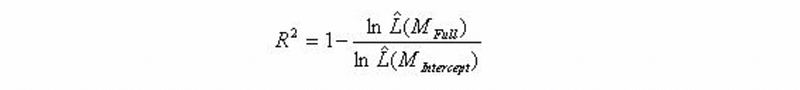
See a more detailed explanation here (from UCLA).
To select the best logistic model, we can use the AIC or the BIC because these concepts hold for the logistic model.