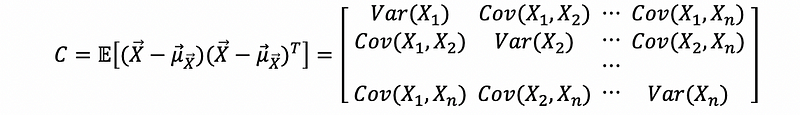Statistics for Application 3 | Function of Random Variables, Function of Random Vectors
Statistics for Application 3 | Function of Random Variables, and Function of Random Vectors

- Recall: Probability Functions
(1) Probability Mass Function (PMF)
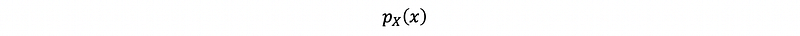
(2) Probability Density Function (PDF)

(3) Cumulative Density Function (CDF)
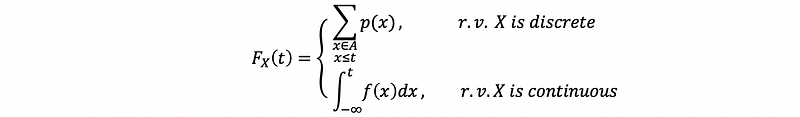
(4) Joint Probability Density Function
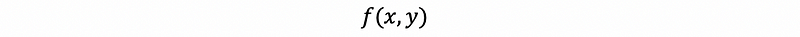
(5) Marginal Probability Density Function
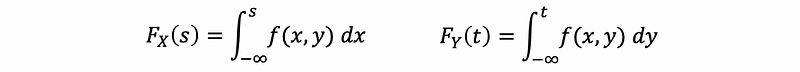
(6) Joint Cumulative Density Function
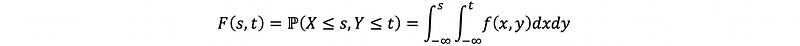
(7) Joint Probability Mass Function
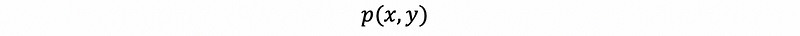
(8) Marginal Probability Mass Function

(9) Definition of Independent Random Variables
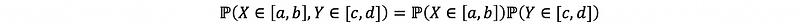
(10) Properties of Independency
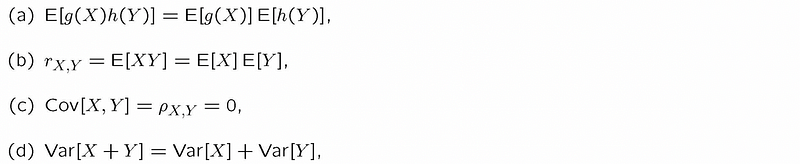
2. Function of Random Variables
(1) CDF Yielding Multiplied Continuous Random Variables
If W = aX, then,
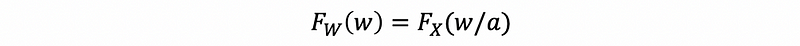
(2) PDF Yielding Multiplied Continuous Random Variables
If W = aX, then,
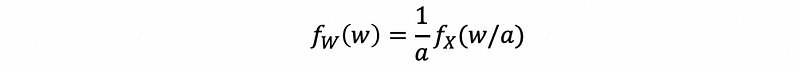
(3) CDF Yielding Continuous Random Variables Adding Constant
If W = X+b, then,
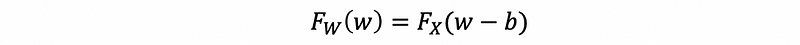
(4) PDF Yielding Continuous Random Variables Adding Constant
If W = X+b, then,
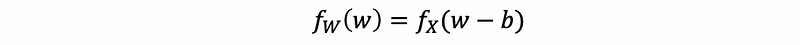
(5) CDF of the Sum of Two Random Variables
If W = X+Y, then,
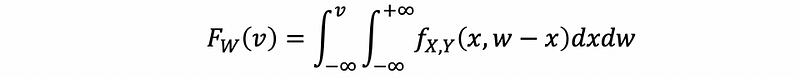
(6) PDF of the Sum of Two Random Variables
If W = X+Y, then,
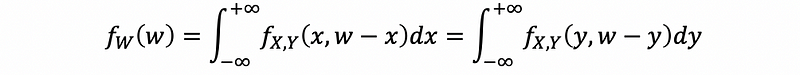
(7) PDF of a Function with Two Random Variables
If W = g(X, Y), then,
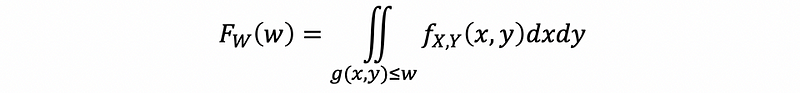
(8) PDF of the maximum of Two Random Variables
If W = max{X, Y}, then,
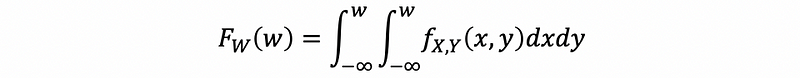
(9) CDF of an Inverse Uniform Random Variable
If W = F^(-1)(X) and X ~Unif(0, 1), then,
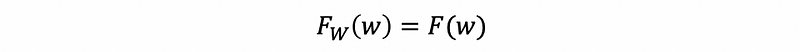
3. PMF and PDF with Conditional Event
(1) Conditional Joint PMF
For any given event B, a region of X, Y plane with ℙ(B) > 0,
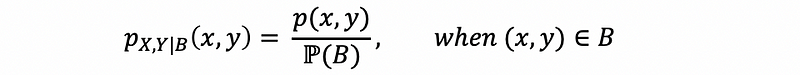
Or 0 otherwise.
(2) Conditional Joint PDF
For any given event B, given a joint function f(x, y) with ℙ(B) > 0,
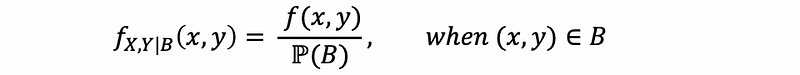
Or 0 otherwise.
(3) Conditional Expected for Discrete Random Variables
If W = g(X, Y), then,
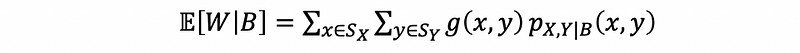
(4) Conditional Expected for Continuous Random Variables
If W = g(X, Y), then,
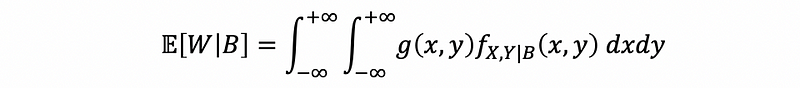
4. PMF and PDF with Conditional Random Variable
(1) Conditional PMF
For any event Y = y such that p(y) > 0, then the conditional PMF of X given Y = y is,
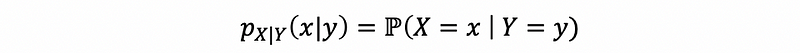
This is also,

(2) Conditional PDF
For y such that f(y) > 0, then the conditional PDF for X given {Y = y} is,
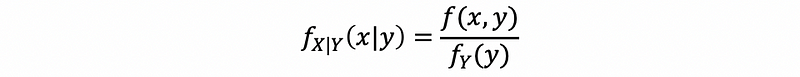
(3) Conditional Expected for Discrete Random Variables
If W = g(X, Y), then,
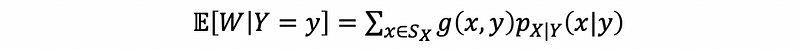
(4) Conditional Expected for Continuous Random Variables
If W = g(X, Y), then,
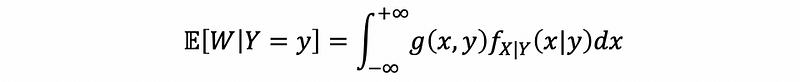
5. Random Vectors
(1) The Definition of the Random Vector
Suppose X1, X2, …, Xn are random variables, then the vector X = [X1 X2 … Xn]’ is then defined as a random vector. When X1 = x1, X2 = x2, …, Xn = xn, then the vector x = [x1 x2 … xn]’ is then defined as a sample of the random vector.
(2) PMF for a Random Vector
The PMF for a random vector X is,
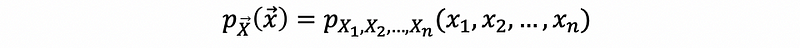
(3) PDF for a Random Vector
The PDF for a random vector X is,
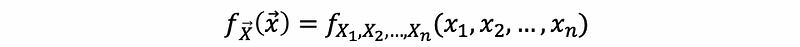
(4) CDF for a Random Vector
The CDF for a random vector X is,
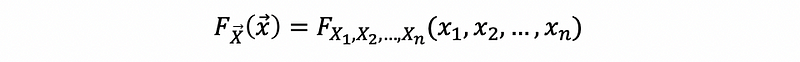
(5) PMF of a Function of Discrete Random Vector
For random variable W = g(X),
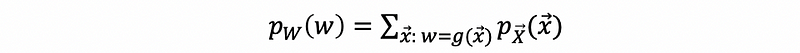
(6) PDF of a Function of Discrete Random Vector
For random variable W = g(X),
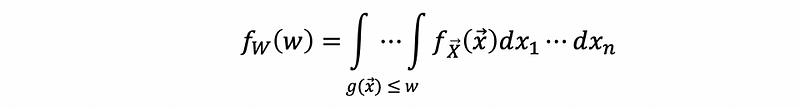
(7) Expectation of a Function of a Discrete Random Vector
For random variable W = g(X),
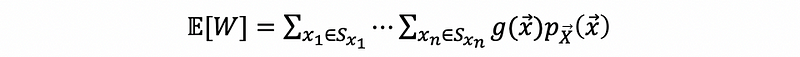
(8) Expectation of a Function of a Continuous Random Vector
For random variable W = g(X),
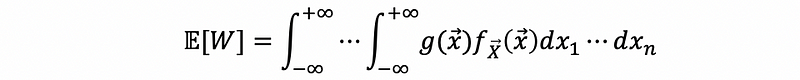
(9) PDF of a Function Yielding Random Vector
For random vector Y = AX + b, and X is a continuous random vector and A is an invertible matrix, then the PDF of Y is,
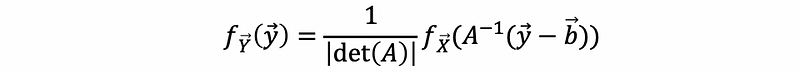
(10) Expectation of Random Vector
The expectation value of a random vector X is a column vector, then,
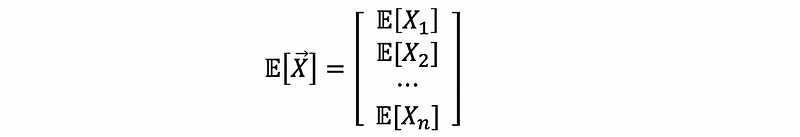
(11) Correlation Matrix of Random Vector
The correlation matrix of a random vector X is an n × n matrix R, which is defined as,
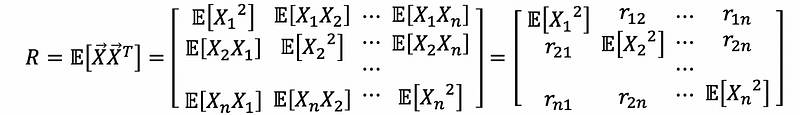
(12) Variance-Covariance (Cross-Correlation) Matrix of Random Vector
The variance-covariance matrix of a random vector X is an n × n matrix C, which is defined as,